A Breakthrough in Understanding Planet Formation
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery by capturing the moment a planet forms around a star other than the Sun. This remarkable observation provides a unique glimpse into the early stages of planetary development, offering insights into how our own solar system came to be.
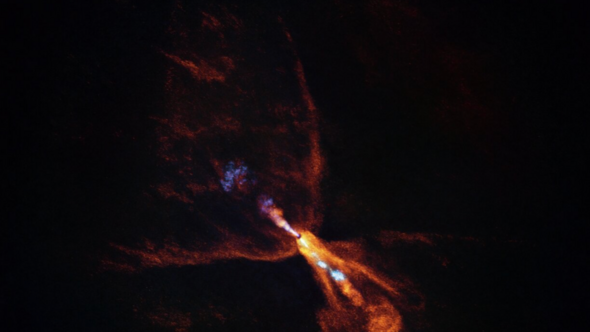
The findings were made possible through the combined efforts of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory in Chile. These powerful instruments allowed scientists to observe the formation of the first specks of planet-forming material—hot minerals that are just beginning to solidify. The discovery is considered a significant step forward in understanding the processes that shaped our solar system billions of years ago.
Professor Merel van ‘t Hoff, one of the researchers involved in the study, described the findings as “a picture of the baby Solar System.” She emphasized that this particular system offers a rare opportunity to study the early stages of planetary formation, which are otherwise difficult to observe.
Observing the Birth of a New World
The planet-forming activity was observed around a yellow dwarf star named HOPS-315, located approximately 1,300 light-years away from Earth. This young star is still in the process of forming, surrounded by a disk of gas and dust. Researchers focused on this disk and discovered solid particles condensing within it—early signs of planet formation.
“This is the first time we have identified the earliest moment when planet formation is initiated around a star other than our Sun,” said Professor Melissa McClure, another key researcher in the study. Her team’s findings suggest that the process of planet formation may be more common than previously thought.
McClure explained that the detection of hot mineral condensation around other stars had never been observed before. This raised questions about whether such a process was unique to our solar system or a universal feature of planetary formation. Now, with this new evidence, scientists believe that this could be a common occurrence during the early stages of planet formation.
Implications for Our Understanding of the Universe
The discovery has major implications for our understanding of how planets form and evolve. By studying systems like HOPS-315, astronomers can gain a better grasp of the conditions that led to the formation of Earth and other planets in our solar system. It also opens up new possibilities for exploring exoplanets and their potential to support life.
This breakthrough highlights the importance of advanced telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope, which allows scientists to peer deeper into space and observe phenomena that were once beyond our reach. As technology continues to advance, we can expect more discoveries that will reshape our understanding of the universe.
Future Research and Exploration
With this new knowledge, researchers are now looking to study similar systems in greater detail. They hope to uncover more clues about the conditions that lead to planet formation and how these processes vary across different star systems.
The study also underscores the value of international collaboration in astronomy. By combining data from multiple observatories and space missions, scientists can achieve a more comprehensive view of the cosmos. This collaborative approach is essential for making further discoveries and answering some of the most fundamental questions about our place in the universe.
As we continue to explore the vastness of space, each new discovery brings us closer to understanding the origins of our solar system and the potential for life beyond Earth.